Cisco CCNP - OSPF Single Area - Lab 1
This article will describe the first CCNP MPLS lab.
Initial Configuration
Lab Details
The simulator used for this article was PNETLAB and the devices are running the Cisco IOSv image.
Getting Command Line Access
Answer no to the initial configuration dialogue.
% Please answer 'yes' or 'no'.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: nChange from user mode to privileged mode
Router>enable
Router#Change to configure mode
Router#configure
Configuring from terminal, memory, or network [terminal]? terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#Adding Base Configuration
configure terminal
hostname R1
ip domain-name infoitech.co.ukSecuring Access
configure terminal
line console 0
password cisco
loginRequire a password when logging in to the console.
configure terminal
line aux 0
password cisco
loginRequire a password when logging in to the Aux Port.
configure terminal
service password-encryptionEncrypt all passwords.
Saving the Configuration
copy running-config startup-config
startup-configR1#copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]? startup-config
Building configuration...
[OK]Configuring Interfaces
Let's configure the interfaces according to the diagram below.
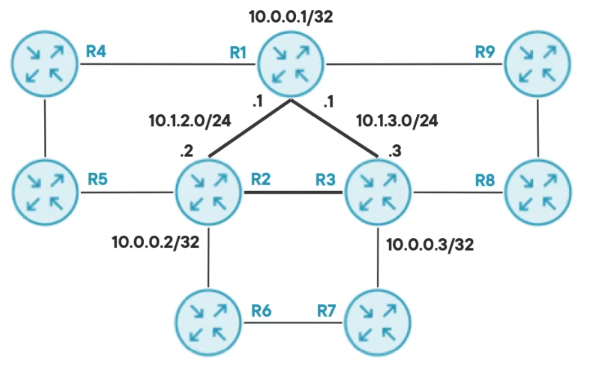
configure terminal
int lo0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255Configuring the Loopback interface.
configure terminal
interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
description "R1 to R2"
no shutdown
Interface facing R2
configure terminal
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
description "R1 to R3"
no shutdown
Interface facing R3
show interfaces description Interface Status Protocol Description
Gi0/0 up up "R1 to R2"
Gi0/1 up up "R1 to R3"
Gi0/2 admin down down
Gi0/3 admin down down
Lo0 up up Repeat the steps above for R2 and R3 changing the commands accordingly.
Show Interface Configuration
To show the configuration of an interface use the command below.
show run interface gigabitEthernet 0/0Building configuration...
Current configuration : 202 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description "R3 to R1"
ip address 10.1.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf 1 area 0
duplex auto
speed auto
media-type rj45
no cdp enable
end
Show Routing Table
To show the installed routing table use the command below.
show ip routeCodes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.3/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 10.1.3.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0Configuring OSPF
Enabling OSPF
Let's enable debug mode on OSPF hello messages.
debug ospf hello Let's enable the OSPF process.
configure terminal
router ospf 1The number 1 is the process number and is local to the router. The purpose of the process is to allow for multiple OSPF instances on the router.
OSPF Authentication
In a public network, it is simple for an unauthorized device to emulate an OSPF router and potentially disrupt network operation by presenting false information. To provide protection from this situation let's configure the most secure and recommended MD5 authentication.
MD5 authentication passwords do not have to be the same throughout an area. However, they do need to be the same between neighbours.
configure terminal
interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco_ospf
interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco_ospf
interface lo0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco_ospfEnabling MD5 password in R1 all interfaces.
The key ID allows the routers to reference multiple passwords. This makes password migration easier and more secure. For example, to migrate from one password to another, configure a password under a different key ID and remove the first key.
configure terminal
router ospf 1
area 0 authentication message-digestEnabling MD5 password in R1 all interfaces in area 0
The area authentication message-digest command in this configuration enables authentications for all of the router interfaces in a particular area. You can also use the ip ospf authentication message-digest command under the interface to configure MD5 authentication for the specific interface. This command can be used if a different authentication method or no authentication method is configured under the area to which the interface belongs. It overrides the authentication method configured for the area. This is useful if different interfaces that belong to the same area need to use different authentication methods.
R1#show run interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 228 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description "R1 to R2"
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 7 121A0C041104330B393B22
ip ospf network point-to-point
duplex auto
speed auto
media-type rj45
end
Interface configuration with password hash enabled and MD5 authentication enabled for OSPF.
OSPF Network Configuration
OSPF can be configured on an interface in two ways. In the example below, OSPF is configured using subnets, and the interfaces configured with the specified subnets will be OSPF enabled.
This LAB uses a single OSPF area 0 on the CORE routers.
The network command enables OSPF in any interface that matches the subnet and wildcard mask. A wildcard 0.0.0.0 will match only a single IP address.
configure terminal
router ospf 1
network 10.1.2.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.1.3.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
As seen in the output from the command below. The interface GigabitEthernet0/1 OSPF configuration was attached via a network statement.
show ip ospf interfaceGigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.3.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 10.0.0.1, Interface address 10.1.3.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:06
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)OSPF Interface Configuration
OSPF can also be configured on the interface. Let's configure an interface in R2 using the per-interface commands.
configure terminal
interface gigabitEthernet0/0
ip ospf 1 area 0
exit
Using the command below, we can see that the interface gigabitEthernet0/0 is reporting that OSPF was attached via Interface Enable.
show ip ospf interfaceGigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.2.2/24, Area 0, Attached via Interface Enable
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.2, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Enabled by interface config, including secondary ip addresses
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 10.0.0.2, Interface address 10.1.2.2
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:05
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
OSPF Network Type
By default, the OSPF network type is set as BROADCAST and it needs to be changed to point-to-point which is considered best practice.
When two routers are directly connected by Ethernet, it is preferable to configure the interface as point-to-point because no DR is required and the adjacency can be formed more quickly.
The command below shows the OSPF details on an interface.
show ip ospf interfaceGigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.3.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 10.0.0.1, Interface address 10.1.3.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:06
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)To change the type we use the commands below.
configure terminal
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip ospf network point-to-point
exit
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip ospf network point-to-pointGigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.3.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.1, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:05
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)Since we enabled debug mode the router will notify us about hello messages sent to neighbors.
*Nov 20 15:37:57.904: OSPF-1 HELLO Gi0/0: Send hello to 224.0.0.5 area 0 from 10.1.2.1
*Nov 20 15:38:02.425: OSPF-1 HELLO Gi0/1: Send hello to 224.0.0.5 area 0 from 10.1.3.1A full analysis of the Hello Message can be found at this link.
OSPF Adjacency
The routers will then exchange link state database information and establish an adjacency. A full breakdown of the process can be found on this link.
*Nov 21 14:00:22.138: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading DoneWe can use the command below to check the OSPF database and all the Router LSAs. For more information on LSA types check this link.
show ip ospf database routerOSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1297
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 10.0.0.1
Advertising Router: 10.0.0.1
LS Seq Number: 8000004A
Checksum: 0x143E
Length: 72
Number of Links: 4
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 10.0.0.3
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.1.3.1
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.1.3.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 10.0.0.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.1.2.1
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.1.2.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
LS age: 1643
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 10.0.0.2
Advertising Router: 10.0.0.2
LS Seq Number: 80000041
Checksum: 0xEAB8
Length: 48
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 10.0.0.1
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.1.2.2
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.1.2.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
LS age: 1298
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 10.0.0.3
Advertising Router: 10.0.0.3
LS Seq Number: 80000049
Checksum: 0xFA9B
Length: 48
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 10.0.0.1
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.1.3.3
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.1.3.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1R1 OSPF LSA Database
BFD with OSPF Network
To configure BFD with OSPF, we must enable it on the interface. This link explains the BFD protocol in more detail.
configure terminal
interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
bfd interval 50 min_rx 50 multiplier 3R1 BFD Interface Configuration
And enable it for all interfaces.
configure terminal
router ospf 1
bfd all-interfacesEnabling BFD in all OSPF Interfaces
With the command below we can check the session details.
show bfd neighbors detailsIPv4 Sessions
NeighAddr LD/RD RH/RS State Int
10.1.2.2 1/1 Up Up Gi0/0
Session state is UP and using echo function with 50 ms interval.
Session Host: Software
OurAddr: 10.1.2.1
Handle: 1
Local Diag: 0, Demand mode: 0, Poll bit: 0
MinTxInt: 1000000, MinRxInt: 1000000, Multiplier: 3
Received MinRxInt: 1000000, Received Multiplier: 3
Holddown (hits): 0(0), Hello (hits): 1000(960)
Rx Count: 617, Rx Interval (ms) min/max/avg: 3/42326/939 last: 182 ms ago
Tx Count: 967, Tx Interval (ms) min/max/avg: 2/1205/870 last: 350 ms ago
Elapsed time watermarks: 0 0 (last: 0)
Registered protocols: OSPF CEF
Uptime: 00:07:29
Last packet: Version: 1 - Diagnostic: 0
State bit: Up - Demand bit: 0
Poll bit: 0 - Final bit: 0
C bit: 0
Multiplier: 3 - Length: 24
My Discr.: 1 - Your Discr.: 1
Min tx interval: 1000000 - Min rx interval: 1000000
Min Echo interval: 50000
We can also check if BFD is enabled in OSPF with the command below.
R1#show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 10.0.0.1
...
BFD is enabled
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 3
Area has message digest authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:09:34.525 ago
SPF algorithm executed 4 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 3. Checksum Sum 0x02411D
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
And finally we can confirm if BFD is enabled with the OSPF interface command.
R1#show ip ospf interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.2.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.1, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, BFD enabled
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:04
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 1 msec, maximum is 1 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 10.0.0.2
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
Cryptographic authentication enabled
Youngest key id is 1Disabling OSPF on Interface
OSPF was configured on the interface below.
R3#show run interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 202 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description "R3 to R1"
ip address 10.1.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf 1 area 0
duplex auto
speed auto
media-type rj45
no cdp enable
end
To disable OSPF in an interface the commands below can be used.
configure terminal
interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
no ip ospf 1 area 0*Nov 24 20:52:42.133: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detachedFinal Steps
To complete the lab let's enable OSPF in all the interfaces facing each router.
R1#show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Gi0/1 1 0 10.1.3.1/24 1 P2P 1/1
Gi0/0 1 0 10.1.2.1/24 1 P2P 1/1R1 OSPF Interfaces
R2#show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Gi0/1 1 0 10.2.3.2/24 1 P2P 1/1
Gi0/0 1 0 10.1.2.2/24 1 P2P 1/1R2 OSPF Interfaces
R3#show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Gi0/1 1 0 10.2.3.3/24 1 P2P 1/1
Gi0/0 1 0 10.1.3.3/24 1 P2P 1/1R1 OSPF Interfaces
OSPF & Loopback Interfaces
Let's make the loopback interfaces reachable adding OSPF config to them as well. Repeat the configuration below in all routers.
configure terminal
int lo0
ip ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
Final Routing Table
The routing table in the routers should have the below routes installed by OSPF.
R1#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.0.0.2/32 [110/2] via 10.1.2.2, 00:06:01, GigabitEthernet0/0
O 10.0.0.3/32 [110/2] via 10.1.3.3, 00:17:57, GigabitEthernet0/1
C 10.1.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 10.1.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 10.1.3.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 10.2.3.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.3.3, 00:33:54, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/2] via 10.1.2.2, 00:30:40, GigabitEthernet0/0R1 Full Routing Table
R2#show ip route ospf
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
O 10.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 10.1.2.1, 00:05:20, GigabitEthernet0/0
O 10.0.0.3/32 [110/2] via 10.2.3.3, 00:19:16, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 10.1.3.0/24 [110/2] via 10.2.3.3, 00:31:49, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/2] via 10.1.2.1, 01:22:19, GigabitEthernet0/0R2 OSPF Injected Routes
R3# show ip route ospf
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
O 10.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 10.1.3.1, 00:06:26, GigabitEthernet0/0
O 10.0.0.2/32 [110/2] via 10.2.3.2, 00:08:26, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 10.1.2.0/24 [110/2] via 10.2.3.2, 00:32:55, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/2] via 10.1.3.1, 00:49:03, GigabitEthernet0/0R3 OSPF Injected Routes
As seen all Loopback interfaces are reachable and the routers have alternate routes to each other's subnets.
Troubleshooting

Interface Down
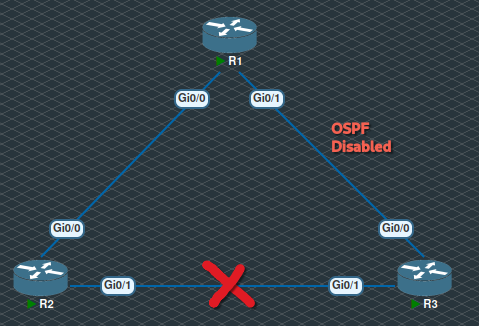
Consider the link between R2 and R3 is down and OSPF is disabled on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0 facing R1.
The routing table will look like this. And we will only be able to reach 10.1.3.1.
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.3/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 10.1.3.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
R3#ping 10.1.3.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.3.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/6/8 ms
R3#ping 10.1.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)When OSPF is enabled, the adjacency is formed and the route table is updated. A new OSPF route has been added allowing us now to ping R2 subnet 10.1.2.0/24.
R3#conf t
R3(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
3(config-if)#ip ospf 1 area 0
*Nov 24 21:06:26.934: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.3/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.1.2.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.3.1, 00:01:22, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 10.1.3.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
R3#ping 10.1.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 6/7/9 msLab Startup-Config
Below are the configuration files of the routers used in this lab.
Resources


![Infoitech - [B]logging](https://blog.infoitech.co.uk/content/images/2021/04/youtube-small-cover-1.png)


